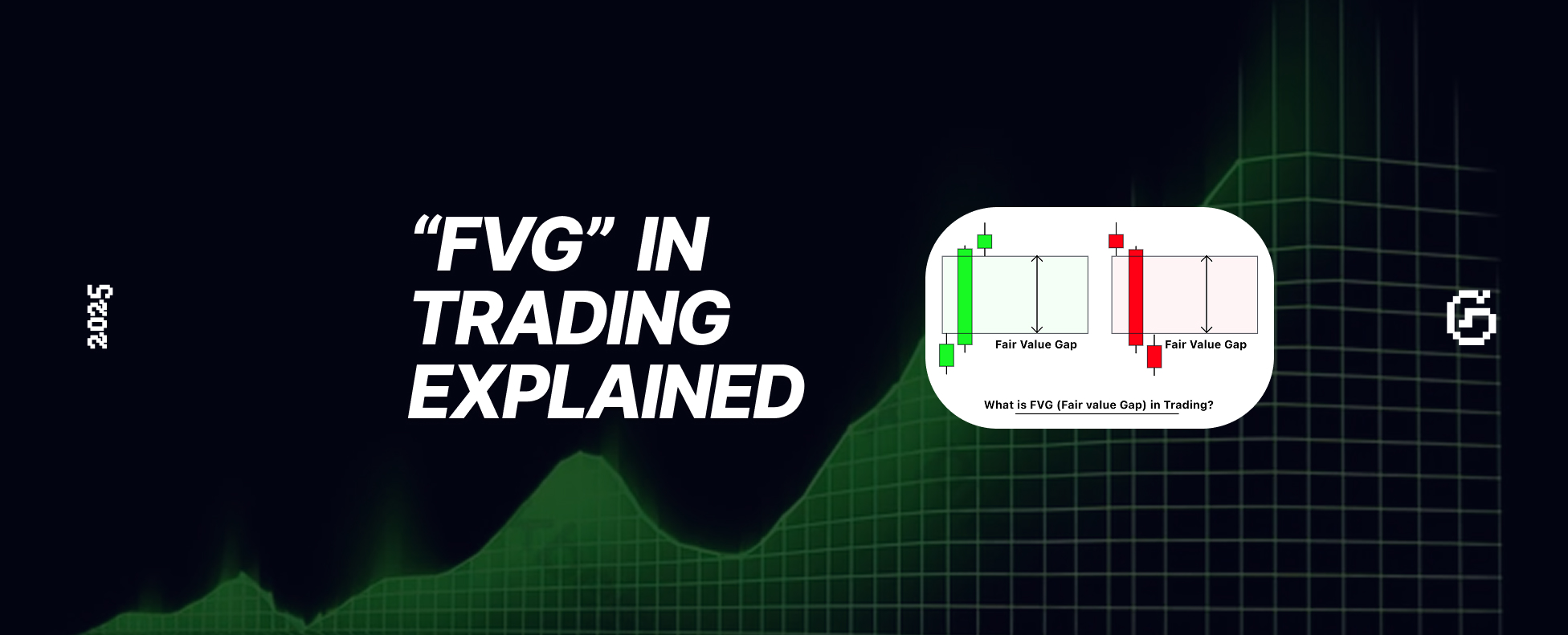
If you’ve ever come across the term “Fair Value Gap (FVG)” in trading, you might’ve wondered what it really means and why it matters.
In short, the fair value gap is a price imbalance left on the chart when large institutional orders move the market too quickly, leaving behind untraded price areas.
Understanding this concept can drastically improve your entries, exits, and risk management — especially if you follow Smart Money Concepts (SMC).
In this guide, we’ll break down what the fair value gap concept is, how it works, and how you can trade FVGs effectively using tools like GASPNTRADER.
What Is a Fair Value Gap (FVG)?
A Fair Value Gap represents an imbalance between buyers and sellers on a candlestick chart.
It occurs when price moves so quickly in one direction that no counter-trades occur within a certain price range.
In simpler terms:
A fair value gap is the empty space between consecutive candles that shows where price didn’t trade efficiently.
This gap often acts as a magnet for price, as the market later returns to “fill” the imbalance.
Understanding the Fair Value Gap Concept
In a normal, balanced market, every buyer has a seller.
However, when institutional traders execute massive orders, price can jump rapidly, creating an inefficient area where few transactions happen.
That area — usually between the high of one candle and the low of another — forms the FVG.
Traders interpret this as:
- A sign of strong institutional activity (large buy/sell imbalance)
- A potential retracement zone where price may return
- A high-probability entry area once price fills the gap
The Fair Value Gap Candlestick Pattern
Let’s visualize this with a simple example.
Imagine three consecutive candles on a chart:
- Candle A — bearish
- Candle B — large bullish impulse
- Candle C — smaller bullish continuation
If the high of Candle A is below the low of Candle C, there’s a visible gap between them.
That’s your fair value gap candlestick pattern — an area price may later revisit to fill inefficiencies.
Key Features of the FVG Pattern:
- Formed during strong impulsive moves
- Indicates unbalanced order flow
- Serves as a retracement or reaction zone

Why Fair Value Gaps Matter
Fair Value Gaps help traders understand where price might correct before continuing in its main direction.
Institutions tend to fill these gaps to restore equilibrium before making the next move.
Benefits of identifying FVGs:
- High-probability entries: Wait for price to fill the gap before entering.
- Improved stop-loss placement: Gaps often mark strong reaction zones.
- Trend continuation signals: Once filled, price often resumes its direction.
Fair Value Gap in Forex
In forex trading, fair value gaps are common on major currency pairs during high-volatility sessions — such as London or New York open.
When institutions execute massive orders, EUR/USD or GBP/USD can create quick surges, leaving imbalances (FVGs) behind.
For example:
- A bullish impulse on EUR/USD creates a gap.
- Price later retraces into the gap zone.
- On rejection, traders enter long positions aligned with institutional order flow.
This is why the fair value gap forex strategy is popular among SMC traders — it gives clear entry levels and targets.

The History of Fair Value Gaps
The fair value gap concept comes from Smart Money Concepts (SMC) and ICT (Inner Circle Trader) theory, which focus on reading institutional footprints.
Michael J. Huddleston (ICT) popularized the term “Fair Value Gap,” teaching traders how these inefficiencies represent liquidity voids that price seeks to rebalance.
Over time, this approach became a core idea in institutional trading education, influencing thousands of traders across forex, crypto, and futures markets.
How the Fair Value Gap Works
Here’s a simplified explanation of how it works step-by-step:
-
Institutional Entry:
Big players enter with large buy or sell orders, pushing price sharply in one direction. -
Imbalance Forms:
The market moves too fast for opposite orders to fill, creating a gap. -
Retracement:
Price later returns to that unbalanced area to “fill” missing orders. -
Continuation or Reversal:
After filling the gap, price either continues in the original direction or reverses depending on liquidity.

How to Identify Fair Value Gaps
Follow these steps to identify a valid FVG:
Step 1. Spot Three Consecutive Candles
Look for a strong impulsive candle (Candle 2) between two others (Candle 1 and Candle 3).
Step 2. Check for Price Displacement
If Candle 1’s high is below Candle 3’s low, the space in between is the fair gap value.
Step 3. Draw Your Zone
Mark the range between Candle 1’s high and Candle 3’s low as your FVG zone.
Step 4. Wait for Price to Return
When price comes back to this zone, observe rejection or continuation for trade confirmation.
Fair Value Gap Entry Strategy
Here’s how to use the fair value gap entry strategy effectively:
-
Identify FVG after an impulsive move.
Example: Strong bullish candle with a visible gap. -
Wait for retracement into the gap zone.
Don’t enter immediately after formation. -
Confirm entry with reaction.
Look for reversal candlestick patterns or lower timeframe structure breaks. -
Set risk and targets.
- Stop loss: beyond the FVG
- Take profit: at liquidity zones or opposing FVGs
Example trade:
Price rallies → creates a bullish FVG → retraces → rejects → entry confirmation → continuation to new highs.

FVG Types: Bullish vs Bearish Fair Value Gaps
| Type | Description | Market Behavior |
|---|---|---|
| Bullish FVG | Occurs after strong upward move | Price retraces into gap then continues higher |
| Bearish FVG | Occurs after strong downward move | Price retraces into gap then continues lower |
Example:
A bullish FVG appears after a large green candle. When price comes back, traders look for long setups at the gap’s midpoint.
Combining FVG with Other Tools
FVGs work best when combined with other SMC tools such as:
- Order Blocks — confirm institutional zones
- Break of Structure (BOS) — validate trend continuation
- Liquidity sweeps — detect stop-hunt reversals
- Higher Timeframe Confluence — align with larger trends
When all align, FVG-based setups can deliver exceptional risk-to-reward ratios.
Common Mistakes with Fair Value Gaps
- Entering too early before price fills the gap.
- Trading every gap — focus on strong impulsive moves only.
- Ignoring context — use confluence from structure and liquidity.
- Forcing trades — not every imbalance is worth trading.
Patience and confirmation are key to consistent success.
Integrating FVG Analysis in GASPNTRADER
GASPNTRADER helps you journal and analyze fair value gap trades effortlessly.
1. Tag FVG-Based Trades
Use labels like “Bullish FVG” or “Bearish FVG” inside your journal for data tracking.
2. Measure Win Rate by Setup
Over time, you’ll identify which FVG setups yield the best results for your trading style.
3. Review FVG Reactions
Use the overview dashboard to visualize reaction zones, entry precision, and R:R ratios.
4. Build Data-Driven Confidence
By journaling your FVG trades, you’ll gain statistical insights into what works best — turning concepts into proven edges.
Final Thoughts
The Fair Value Gap is one of the most powerful concepts in modern technical analysis.
It bridges the gap (literally) between price action and institutional intent.
By understanding how the fair value gap works, learning to spot the fair value gap candlestick pattern, and applying a clear entry strategy, you can trade alongside smart money — not against it.
Track your FVG trades with GASPNTRADER and turn theory into performance data that helps refine your edge over time.